The Impact of the Biggest Pharma Merger You’ll Wish Never Happened on Drug Prices
In recent years, we’ve seen some transformational pharma mergers that promise to change the landscape of drug development and pricing. However, one merger stands out, leaving many people wishing it never took place. This merger has raised eyebrows and questions about its long-term impact—especially on drug prices. When mega-pharmaceutical companies combine, the expectation often is that efficiency and innovation will follow. Unfortunately, the reality can be starkly different.
When examining the impact of significant pharma mergers, you need to consider the pathways that lead to shifts in drug prices. Here’s why this particular merger should concern you:
Diminished Competition
One of the chief effects of any major merger, including the biggest pharma merger, is a substantial reduction in competition. With fewer companies in the market, it becomes easier for the newly formed entity to set prices without fear of being undercut. This often leads to:
- Increased drug prices for consumers
- Limited choices in medication options
- Higher out-of-pocket expenses for patients
Focus on Profit over Patient Care
After a merger, the newly formed company may shift its focus from patient care to profit maximization. This clearer focus often results in:
- Less investment in research and development for new medications
- Higher costs associated with existing treatments
- A potential decrease in the quality of care that patients receive
This focus on profit can lead to a real disconnect between what patients need and what is available in the market.
Increased Bargaining Power
The merger creates a larger entity with more negotiating power. With this increased clout, the company can negotiate terms with suppliers, pharmacy benefit managers, and even healthcare providers that may not always prioritize lower costs for consumers. The result can lead to unrealistically high prices for medications that your health plan struggles to cover.
The Ripple Effect on Healthcare Systems
When drug prices rise, healthcare systems can feel the pressure. This change often results in:
- Higher insurance premiums for consumers
- Increased strain on publicly funded healthcare systems
- A higher number of uninsured patients due to rising costs
As drug prices continue to climb, the financial burden shifts from the pharmaceutical companies to consumers and healthcare systems, creating a complex web of consequences.
Immediate Access Challenges
Many patients rely on medications to manage chronic illnesses. When a major merger takes place, accessibility to these essential medications can dramatically change. Patients may find:
- Longer waiting times for prescriptions
- Increased co-pays or out-of-pocket expenses
- Limited stock availability in pharmacies
This lack of immediate access can severely impact patient compliance and overall health outcomes.
What Can Be Done?
Your voice matters. Here’s how you can engage with this crucial issue:
- Stay informed about changes in drug prices stemming from mergers.
- Advocate for transparency in pricing for medications.
- Support policies that encourage competition among drug manufacturers.
For more insights on the direct effects of pharmaceutical mergers, explore destinations like NBER and Brookings Institution.
As we’ve seen, the implications of the biggest pharma merger are far-reaching and affect drug prices in ways that can have life-altering consequences. For many, navigating these waters may feel daunting, but awareness and action can help mitigate the most adverse effects. Ultimately, it’s about ensuring prescription medication remains accessible and affordable for everyone.
Evaluating the Ethical Implications of Large-Scale Pharma Mergers
The rapid growth of the pharmaceutical industry has led to a series of high-profile mergers that have raised numerous ethical questions. While these mergers can create benefits in terms of increased resources and enhanced drug development capabilities, they often come with consequences that can adversely affect healthcare systems and patients worldwide.
One primary ethical implication of large-scale pharmaceutical mergers is the potential for reduced competition. When two major companies merge, they can eliminate rivals, leading to a monopoly or oligopoly situation. This monopolistic power can result in:
- Increased drug prices
- Limited access to essential medications
- Reduced incentives for innovation
As a result, consumers may face higher expenses for medications they need, which can lead to significant challenges in managing their health conditions. The issue of affordability becomes even more pressing when considering that many people in the world already struggle to pay for their medications.
Another point of concern is how these mergers can affect research and development (R&D) priorities. Large pharmaceutical companies may prioritize profits over public health needs, shifting focus away from essential but less profitable drugs. This can lead to:
- Neglect of rare diseases
- Fewer investments in antibiotic development
- Less funding for public health initiatives
Instead of focusing on groundbreaking treatments, combined entities might concentrate on lifestyle drugs that drive higher profits. The repercussions can be significant. For instance, the threat of antibiotic resistance continues to grow, and the lack of financial motivation to develop new antibiotics could worsen this public health crisis.
The loss of workforce diversity is another ethical predicament caused by these mergers. When two pharmaceutical giants join forces, layoffs often follow. A diverse workforce brings varied perspectives, which can lead to better solutions in medication development and patient care. The reduction in staff diversity can close the door on innovative ideas and limit the ways companies approach complex health challenges.
Moreover, there is a growing concern about transparency and accountability in the pharmaceutical industry. Large mergers can lead to enormous influence over regulatory bodies, which raises questions about the integrity of approval processes and the adequacy of safeguards for patients. Without scrutiny, potential negative effects on public safety may not emerge until it is too late.
Patient involvement is also a significant ethical consideration. The very nature of mergers can lead to prioritizing the shareholders’ interests over patient welfare. It is crucial that patients are treated as active participants rather than passive subjects. Pharmacies must focus on:
- Gathering patient feedback on drug formulations
- Involving patient advocacy groups in product development discussions
- Ensuring clear communication about medication risks and benefits
One example that illustrates these ethical dilemmas is the merger between Pfizer and Allergan, which aimed to create a powerhouse in the pharmaceutical sector. This merger raised eyebrows over how it could potentially affect drug pricing structures and access to critical medications. It ultimately fell through, but the discussions around it shed light on the deep ethical concerns associated with such mergers. For further reading on the implications of this merger, visit Financial Times.
The ethical implications of large-scale pharma mergers extend beyond immediate business concerns and affect patients, healthcare providers, and the overall health ecosystem. As regulatory bodies, policymakers, and pharmaceutical companies navigate these challenging waters, balancing profit motives with ethical responsibilities remains crucial. Advocating for patient-centric policies and transparent processes will be essential to ensure that healthcare priorities align with patient needs and public health goals.
As the industry evolves, promoting a culture of ethics and accountability will be vital in maintaining public trust and ensuring that patients are not forgotten amid corporate interests. This is a call to action for all stakeholders in the pharmaceutical landscape. For ongoing discussions and insights into pharmaceutical ethics, visit Pharmacy Times.
How Mergers Shape Innovation in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry is constantly evolving, driven by the need for new medications and therapies that can improve patient outcomes. One of the significant factors that influence this evolution is the trend of mergers and acquisitions. When companies combine their resources and expertise, they can often accelerate innovation, but there are both pros and cons to consider.
The Role of Mergers in Driving Innovation
Mergers in the pharmaceutical sector can lead to enhanced innovation in several ways:
- Pooling Resources: When two companies merge, they combine their financial and human resources. This allows for more substantial investments in research and development (R&D), leading to faster and potentially groundbreaking discoveries.
- Sharing Knowledge: With diverse teams coming together, the exchange of ideas and expertise becomes richer. This collaboration can lead to innovative approaches that neither company could have achieved alone.
- Access to New Markets: Mergers can help companies gain access to new geographical markets. By entering these markets, they can understand diverse patient needs and focus on innovative solutions tailored to specific populations.
Challenges Post-Merger
Despite the potential for innovation, the post-merger landscape can present numerous challenges:
- Integration Issues: Merging two different corporate cultures can hinder productivity and innovation. Employees may feel uncertain about their roles, which can stifle creativity.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The pharmaceutical industry is heavily regulated. Mergers often require lengthy reviews from government agencies, which can delay the rollout of new products and impact innovation timelines.
- Focus Shift: Sometimes companies become too focused on merging operations, leading to reduced emphasis on projects already in progress, which may impede innovation efforts.
Historical Examples of Mergers Impacting Innovation
There have been many notable mergers that shaped innovation in the pharmaceutical landscape. Here are a couple of examples:
| Year | Merged Companies | Impact on Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Pharmacia and Upjohn | Created new treatment avenues in oncology and cardiology. |
| 2006 | Pfizer and Wyeth | Expanded research capabilities, leading to advances in immunology. |
The Future of Pharma Mergers and Innovation
Moving forward, the impact of mergers on pharmaceutical innovation will likely continue to evolve. With advancements in technology such as big data and artificial intelligence, the potential for innovation through mergers appears promising. Companies are increasingly focusing on biotech collaborations, allowing them to harness cutting-edge scientific discoveries more effectively.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual patient profiles. Mergers that prioritize R&D in this space can lead to significant breakthroughs that enhance patient care and outcomes.
Navigating the Landscape
For stakeholders within the pharmaceutical industry, understanding the dynamics of mergers is crucial. Here are some key strategies that can help navigate this landscape:
- Stay Informed: Keeping up with industry news and trends is vital. Websites like Pharmaceutical News and Medscape can provide valuable insights.
- Foster Collaboration: Building partnerships with other organizations can pave the way for future mergers that enhance innovation.
- Advocate for Employee Engagement: Ensuring that employees are aligned during mergers can significantly reduce confusion and enhance creativity.
Mergers can significantly shape innovation in the pharmaceutical industry, providing both opportunities and challenges. As companies continue to explore such strategies, it’s essential to balance the pursuit of innovation with the complexities that arise from combining diverse entities. With thoughtful planning and implementation, mergers can result in transformative advancements that benefit patients around the world.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Preventing Unwanted Pharma Consolidation
In the ever-evolving landscape of pharmaceuticals, the influence of regulatory bodies plays a crucial role in maintaining market balance and protecting consumer interests. As pharmaceutical companies pursue consolidation through mergers and acquisitions, the need for vigilant oversight grows. Effective regulation helps to prevent unwanted pharma consolidation that may lead to higher drug prices, reduced innovation, and limited patient access to essential medications.
Understanding the Importance of Regulation
Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the EU, and other national agencies, ensure that pharmaceutical companies operate within acceptable standards. Their work encompasses various aspects:
- Ensuring drug safety and efficacy
- Monitoring market competition
- Reviewing drug pricing and access
- Facilitating transparency in clinical trials
The Impact of Pharma Consolidation
When pharmaceutical companies merge, there can be significant implications for consumers and the healthcare system as a whole. Here are a few potential issues that can arise:
- Higher Prices: Mergers can create monopolies, allowing companies to set higher prices without fear of competition.
- Stifled Innovation: With fewer companies operating in the market, the incentive to develop new drugs may diminish.
- Reduced Choices: Consumers may find a smaller selection of medications available, limiting options for treatment.
- Access Barriers: Merged companies might prioritize profit over accessibility, making necessary medications harder to obtain.
The Role of Antitrust Laws
Antitrust laws are essential tools used by regulatory bodies to prevent unwanted pharma consolidation. These laws aim to promote competition and limit monopolistic behavior. In the pharmaceutical industry, they assess mergers through several lenses:
- Market Share Analysis: Regulators examine the market share of merging companies to determine if the consolidation would create a monopoly.
- Price Impact Studies: Antitrust investigations assess how the merger might affect drug prices.
- Innovation Potential: Evaluating whether the merger would inhibit the development of new therapies and technologies.
Engagement with Public and Stakeholders
Regulatory bodies also prioritize engagement with the public and stakeholders in the pharmaceutical industry. Public hearings, stakeholder consultations, and feedback mechanisms are some of the ways they collect insights and concerns. For example:
- Holding open forums allows consumers, healthcare professionals, and industry experts to voice their opinions.
- Online submission portals let stakeholders provide input on proposed mergers.
- Publishing reports and analyses keeps the public informed about ongoing regulatory actions.
Case Studies of Successful Regulatory Intervention
Past cases illustrate how effective regulatory intervention has successfully prevented unwanted consolidation. One significant instance occurred in 2016 when the FDA blocked a proposed merger between two biotech firms. Regulators determined that the merger would result in significant market share overlap, threatening competition and potentially raising drug prices. This action reinforced the importance of regulatory vigilance in the pharmaceutical sector.
Future Trends in Pharma Regulation
Looking ahead, the role of regulatory bodies will likely evolve as pharmaceutical companies continue to seek innovative pathways for consolidation. Key trends include:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Scrutiny | Regulators are likely to impose stricter requirements on mergers, further analyzing impacts on market competition. |
| Global Coordination | International cooperation among regulatory agencies to streamline processes and share information will become more common. |
| Emphasis on Patient Access | Regulators will focus more on the accessibility of drugs, ensuring mergers do not negatively affect patients’ access to medications. |
As the pharmaceutical landscape continues to shift, it remains imperative that regulatory bodies work diligently to prevent unwanted consolidation. By prioritizing competition, consumer protection, and innovation, these agencies can help maintain a healthier market environment. For more insights, explore resources from FDA, EMA, and related organizations.
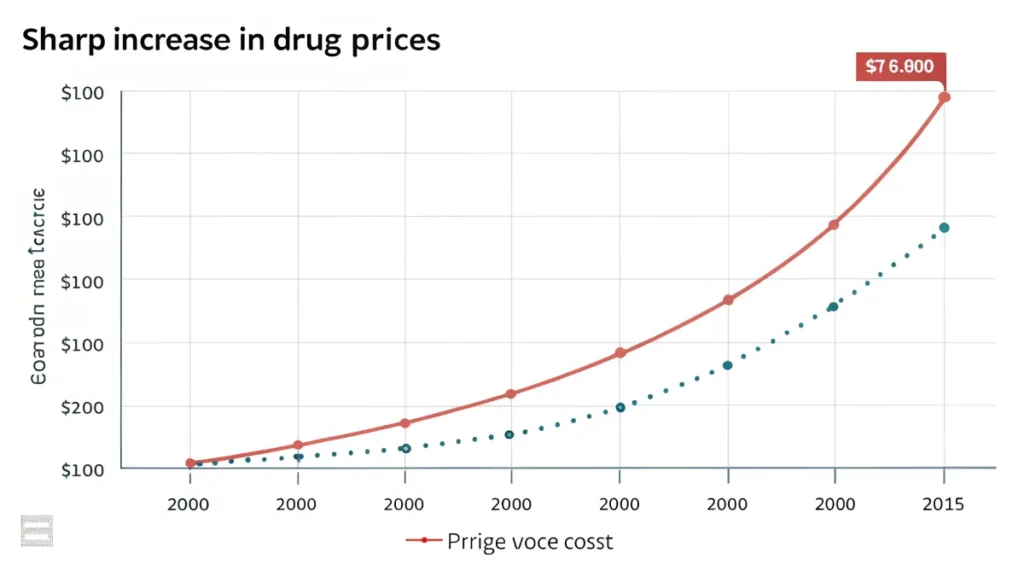
Public Health Consequences of Mergers: What You Need to Know
Mergers in the pharmaceutical industry often make headlines, but the implications stretch far beyond corporate balances. When large pharmaceutical companies merge, the public health consequences can be profound, impacting availability, affordability, and innovation in healthcare. Let’s explore the significant factors you should consider regarding these mergers.
Access to Medications
One direct outcome of pharmaceutical mergers is the impact on access to medications. When two companies combine, they often consolidate their product lines. This can lead to:
- Reduced Competition: With fewer players in the market, competition shrinks, potentially resulting in higher prices for consumers.
- Limited Choices: Mergers may lead to the discontinuation of less profitable drugs, reducing options for patients.
- Geographic Limitations: Merged companies might focus on profitable areas, leaving some regions underserved.
Impact on Drug Pricing
Another major concern is how mergers influence drug pricing. With reduced competition, companies might have less incentive to keep drug prices low. Key concerns include:
- Price Hikes: Merged entities may increase prices significantly, affecting patients who rely on essential medications.
- Insurance Costs: Higher drug prices may lead to increased premiums for health insurance, further burdening consumers.
- Financial Strain: Patients with chronic illnesses might face unmanageable costs, leading to non-adherence to prescribed treatments.
Stifled Innovation
Mergers can also impact research and development budgets. When companies focus on integration, innovation may take a backseat. Consider the following:
- Resource Allocation: Funds that could have fueled new drug research may instead be directed toward merging processes.
- R&D Prioritization: Companies may prioritize profitable products over groundbreaking treatments, stifling advancements in medicine.
- Collaborative Disconnect: Integration can hinder collaborations that spark innovation across different fields.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Public Health
Regulatory bodies such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) keep a watchful eye on pharmaceutical mergers. The implications for public health include:
- Increased Oversight: Mergers often require extensive review, potentially delaying important drug approvals.
- Informed Consent: Patients and healthcare providers must be educated about the implications of these mergers.
- Public Trust: Ongoing mergers can erode public confidence in the pharmaceutical sector.
Case Studies of Impact
Looking at real-world examples can help you understand the effects of mergers. Below is a table that highlights significant mergers and their consequences:
| Merged Companies | Year | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Pfizer and Allergan | 2016 | Failed merger attempted to reduce tax liability but raised questions on pricing strategies. |
| Bristol-Myers Squibb and Celgene | 2019 | Consolidated multiple cancer therapies, impacting drug accessibility. |
| CVS and Aetna | 2018 | Significantly affected how healthcare is delivered, integrating pharmacy and health services. |
Community Health Implications
Community health outcomes can also shift due to pharmaceutical mergers. Here are some potential impacts:
- Public Health Programs: Consolidated companies might withdraw from funding critical community health initiatives.
- Health Disparities: Growth in monopolistic behavior may exacerbate health inequalities across various demographics.
- Chronic Disease Management: Less emphasis may be placed on developing medications for prevalent diseases, such as diabetes or hypertension.
As you can see, the consequences from pharmaceutical mergers extend beyond financial implications and can shape public health in numerous ways. Understanding these impacts helps advocate for better policies and ensures that patient needs are not sidelined. For more information on how mergers affect public health, check out Public Health Ontario or The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Conclusion
The fallout from the biggest pharma merger you’ll wish never happened is multi-faceted and far-reaching. First and foremost, skyrocketing drug prices have become a significant concern for consumers struggling to afford necessary medications. This merger has raised essential questions about the ethical responsibilities of large pharmaceutical companies. Are profit motives outweighing patient needs?
Moreover, the potential for innovation may decrease as competitive pressures dissolve. While one might hope that mergers could pave the way for groundbreaking discoveries, the reality is often more complicated. The unique ideas and spirit found in smaller firms are frequently lost, stifling creativity and advancement.
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in this landscape. Their active involvement is pivotal in preventing unwanted pharma consolidation, ensuring that the marketplace remains healthy and competitive. With this merger, there’s an urgent call for stricter guidelines and transparent practices to protect consumers and the integrity of healthcare.
The public health consequences cannot be ignored. Mergers may lead to reduced access to essential medications, particularly for vulnerable populations. It’s vital for individuals to stay informed about these developments and advocate for policies that prioritize health over profit.
The complexities of this merger illustrate the need for a critical examination of how pharmaceutical companies operate. As engaged citizens, being aware of these dynamics equips us to demand better practices that prioritize innovation, ethics, and public well-being. Your voice matters; use it to influence the future of healthcare.


